
TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs | Must-Solve Questions & Tips for Success
TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs : Quantitative Aptitude plays a pivotal role in the TCS NQT (National Qualifier Test), demanding adept problem-solving abilities. To aid in your preparation, we present 15 significant quantitative aptitude questions drawn from previous years’ papers (PYQs), providing you with a comprehensive insight into the exam format and complexity.

What’s Included in TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs?
- 15 meticulously chosen Quantitative PYQs encompassing key topics
- Topics addressed: Arithmetic, Algebra, Number System, Geometry, and Data Interpretation
- Varied difficulty levels – including easy, moderate, and challenging questions
- Detailed step-by-step solutions for enhanced understanding
Tips and Tricks for Efficiently Solving TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
- Master Key Formulas – Familiarize yourself with essential formulas to accelerate calculations.
- Enhance Mental Math Skills – Boost your calculation speed by minimizing reliance on pen-and-paper methods.
- Employ Approximation Strategies – Use rounding techniques during extensive computations to save time.
- Deconstruct Complex Problems – Tackle questions by simplifying them incrementally to avoid confusion.
- Prioritize Time Management – Establish time constraints for each question during practice sessions.
- Review Previous Year Papers – Gaining insight from past trends can assist in forecasting potential question patterns.
- Regularly Reinforce Concepts – Frequently practice weaker areas to strengthen your understanding.
The 15 Quant PYQs will be provided below. Begin working through them to enhance your accuracy and speed. Consistency in practice will be key to optimizing your performance in the upcoming exam.
Ace the TCS NQT with Our Expert-Led Crash Course – Fast-Track Your Preparation for Success!
TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
1. If 4x²+16y2-12x-40y+34=0, then find the value of (x+y)/(x-y).
- 11
- 9
- 5
- 6
We are given the equation:
4x 2 + 16y 2 −12x−40y+34=0
Step 1: Rewrite in a Standard Form
Dividing by 4 to simplify:
x2 +4y 2 −3x−10y+34/4 =0
x2 −3x+4y2 −10y+8.5=0
Step 2: Complete the Square
For x terms:
(x− 3/2)2 − 9/4
For y terms:
4(y−5/4)2 − 25/4
Rewriting the equation:
(x− 3/2)2 +4(y− 5/4)2 =9
This is the equation of an ellipse centered at (3/2, 5/4).
Step 3: Find (x+y)/(x−y)
Using the formula:
(h−k)/(h+k) = {(3/2) + (5/4)} / {(3/2) – (5/4)}
Solving:
(11/4)/(1/4) = 11
Final Answer: Option (a) 11.
2. Five years ago, Rahul’s age was 5 years less than three times of the sum of the ages of his three children. After five years, his age will become 5 years more than the sum of the ages of his children. Then, what is the present age of Rahul?
- 40 years
- 45 years
- 50 years
- 55 years
Let the present ages be:
Children’s sum = 𝑥
Rahul’s age = 𝑦
Given Conditions:
Five years ago:
3(x−15)−5 = y−5 (Equation 1)
3x−y=45(Equation 1)
After five years:
x+15+5 = y+5 (Equation 2)
x−y=−15(Equation 2)
Solving:
Subtracting (2) from (1):
(3x−y)−(x−y)=45−(−15)
2x=60⇒x=30
Substituting
x=30 in (2):
30−y=−15⇒y=45
Answer:
45
3. If r is the remainder when each of 5264, 5603 and 6168 is divided by the greatest number d (d>1), then d-r is equal to:
- 48
- 45
- 42
- 47
Given numbers: 5264, 5603, 6168
Find the differences:
5603−5264=339
6168−5603=565
6168−5264=904
Find GCD of (339, 565, 904):
gcd(339,565,904)=113
So,
d=113.
Find remainder
r: 5264 mod 113=65
So,
r=65.
Calculate
d−r : 113−65=48
Answer:48
4. The sum of the height and the radius of a solid right circular cylinder is 41 cm. If its total surface area is 2706 cm², then its volume (in cm³) is closest to
- 9568
- 9584
- 10568
- 10584
Given:
Height + Radius = 41 cm
h+r=41
Total Surface Area = 2706 cm²
2πr(h+r)=2706
Substituting h+r=41:
2πr×41=2706
82πr=2706
Using π≈3.1416:
82×3.1416×r=2706
257.12r=2706
𝑟≈ 2706/257.12 ≈ 10.53 cm
Find height:
h=41−r=41−10.53=30.47 cm
Volume Calculation:
V=πr2h
V=3.1416×(10.53)2×30.47
V=3.1416×110.86×30.47
V≈10568 cm³
Final Answer: 10568
5. Height of a right circular cone is increased by 10% and radius of its base is increased by 20%. Find the change in its volume.
- 62.5%
- 58.4%
- 50.2%
- 45.5%
The volume of a right circular cone is given by:
V= 1/3 πr2h
Given Changes:
Height increased by 10% → New height = h′ = 1.1h
Radius increased by 20% → New radius = r ′ = 1.2r
New Volume:
V’ = 1/3π(1.2r)2 (1.2h)
V’ = 1/3π(1.44r2)(1.1h)
V’ = 1/3πr2h * (1.44*1.1)
V’ = V * 1.584
Percentage Increase:
{(V’-V)/V} ×100=(1.584−1)×100 =58.4%
Final Answer: 58.4% TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
6. Two friends Jaya and Vidya walk from M to N, a distance of 27 km, with the speed of 4 km/h and 5 km/h respectively. Vidya reaches the point. N and returned immediately and met Jaya at point “O”. Find the distance between M and O.
- 20 km
- 21 km
- 22 km
- 24 km
Given:
Distance M to N = 27 km
Jaya’s speed = 4 km/h
Vidya’s speed = 5 km/h
Step 1: Time taken by Vidya to reach N and return
27/5 × 2 = 10.8 hours
Step 2: Distance Jaya covers in this time
4 × 10.8 = 24 km
Final Answer: 24 km TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
7. Average weight of 20 students increases by 1.5 kg when a student is replaced by a new student of weight 80 kg. What is the weight of the student who was replaced by the new student?
- 40 kg
- 45 kg
- 50 kg
- 55 kg
Given:
Number of students = 20
Increase in average weight = 1.5 kg
New student’s weight = 80 kg
Step 1: Find total increase in weight
Total increase = Increase in average × Number of students =1.5×20=30 kg
Step 2: Find weight of replaced student
Weight of replaced student = Weight of new student−Total increase =80−30=50 kg
Final Answer: 50 kg TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
8. A and B have some rupees with them. A says to B, “If you give ₹4 to me, I will have two times as many rupees as those left with you.” B replies, “If you give 11 to me, I will have as many rupees as those left with you.” The total number of rupees with A and B is:
- 72
- 88
- 90
- 100
Step 1: Define Variables
Let A have x rupees and B have y rupees.
Step 2: Formulate Equations
Equation 1: x + 4 = 2(y – 4) (If B gives ₹4 to A, A will have twice as many rupees as B)
Equation 2: y + 11 = x – 11 (If A gives ₹11 to B, B will have the same amount as A)
Step 3: Simplify Equations
Equation 1 simplifies to: x – 2y = -12
Equation 2 simplifies to: x – y = 22
Step 4: Solve the System of Equations
Subtract Equation 3 from Equation 4: (x – y) – (x – 2y) = 22 – (-12) => y = 34
Substitute y = 34 into Equation 4: x – 34 = 22 => x = 56
Step 5: Calculate Total Rupees
Total rupees = x + y = 56 + 34 = 90
Final Answer: 90 TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
9. Find the greatest number that will divide 330, 647 and 829 leaving remainders 15, 17 and 19 respectively.
- 15
- 35
- 45
- 55
Given:
We need to find the greatest number d that will divide 330, 647, and 829 leaving remainders 15, 17, and 19 respectively.
Step 1: Convert to a Common Form
The required divisor d must divide the differences:
(330−15),(647−17),(829−19) = 315, 630, 810
Step 2: Find the GCD of 315, 630, and 810
Prime factorizations:
315=32×5×7
630=2×32×5×7
810=2×34×5
Common factors: 3² × 5 = 45
Final Answer: 45 TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs TCS NQT 2025 Quantitative Aptitude PYQs
10.
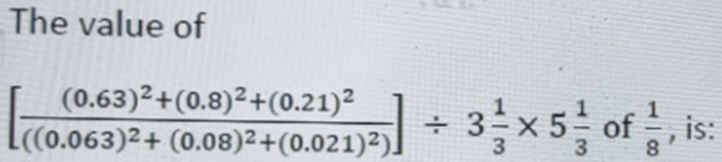
- 45
- 30
- 20
- 15
Step 1: Calculate Numerator
Calculate (0.63)2 + (0.8)2 + (0.21)2 :
(0.63)2 = 0.3969, (0.8)2 = 0.64, (0.21)2 = 0.0441
0.3969 + 0.64 + 0.0441 = 1.081
Step 2: Calculate Denominator
Calculate (0.063)2 + (0.08)2 + (0.021)2 :
(0.063)2 = 0.003969, (0.08)2 =0.0064, (0.021)2 =0.000441
0.003969 + 0.0064 + 0.000441 = 0.01081
Step 3: Form Fraction
Form the fraction 1.081/0.01081 :
1.081/0.01081 = 100
Step 4: Divide by Mixed Number
Convert 3(1/3) to an improper fraction:
3(1/3) = 10/3
Divide 100 by 10/3 :
100 ÷ 10/3 =100 × 3/10 = 30
Step 5: Multiply by Mixed Number
Convert 5(1/3) to an improper fraction:
5(1/3) = 16/3
Multiply 30 by 16/3 :
30 × 16/3 =160
Step 6: Multiply 160 by 1/8:
160 × 1/8 =20
Final Answer: 20
11. A and B invest in a scheme which provides simple interest at the rate of 5 and 6 % per annum for initial capitals less and greater than Rs. 21000 respectively. B’s capital is 20% more than that of A, who invests Rs. 20000. If B invests for two and half years, for how many additional days above three years (the fourth year being a non-leap year) should A invest so that she earns the same amount of interest as B?
- 73
- 146
- 219
- 292
Step 1: Calculate B’s capital
B’s capital is 20% more than A’s capital (Rs 20000). B’s capital = 20000 × 1.20 = 24000
Step 2: Calculate the interest earned by B
Interest earned by B = 24000 × (6/100) × 2.5 = 3600
Step 3: Calculate the time A needs to invest
Let t be the time in years A needs to invest to earn Rs 3600 at 5% per annum on Rs 20000.
20000 × (5/100) × t = 3600
t = 3.6 years
Step 4: Calculate additional days
Additional time = 0.6 years = 0.6 × 365 = 219 days
Final Answer: 219 days
12. Study the following table and answer the question given below:
The table shows the number of boys and girls in five schools A, B, C, D and E
| School | Number of Boys | Number of Girls |
| A | 145 | 82 |
| B | 193 | 160 |
| C | 133 | 101 |
| D | 229 | 190 |
| E | 180 | 127 |
By what per cent is the total number of girls in all the five schools in less than the total number of boys?
- 23%
- 25%
- 33.33%
- 35.75%
Let the number of girls studying in all the five school less than the boys studying in all the five school be x.
Total number of girls in the school= A+B+C+D+E = 82+160+101+190+127 = 660
Total number of boys in the school= A+B+C+D+E = 145+193+133+229+180 = 880
x = 880 – 660 = 220
So percentage lesser
= (220/660) × 100
=33.33%
The percentage of the total number of girls in all the five schools is less than the total number of boys in all the five schools is 33.33%.
13. In a competitive examination, the qualifying percentage of marks is 70%, Komal got 85% of marks in this examination. Renu got 300 marks and failed to qualify the examination by 50 marks. Find the marks obtained by Komal in this examination.
- 405
- 415
- 425
- 435
Step 1: Find the Total Marks
Given that Renu got 300 marks and failed by 50 marks, the qualifying marks are:
300+50=350
Since the qualifying percentage is 70%, we set up the equation:
70/100 × Total Marks = 350
Total Marks = (350 × 100) / 70 = 500
Step 2: Find Komal’s Marks
Komal got 85% of the total marks:
85/100 × 500 = 425
Final Answer: 425
14. Rakesh purchased 4 bats and 10 balls for Rs. 3,650. He sold all the bats at the profit of 30% and balls at a loss of 20%. If his overall profit is Rs. 470, what was the cost price of one bat?
- 550
- 575
- 600
- 625
Given:
- 4 bats + 10 balls = ₹3650
- Bats sold at 30% profit
- Balls sold at 20% loss
- Total profit = ₹470
Step 1: Let cost price of one bat = ₹x, one ball = ₹y
4x+10y=3650
Step 2: Selling Prices
- 4 bats at 30% profit → Selling price = 5.2x
- 10 balls at 20% loss → Selling price = 8y
Total selling price equation:
5.2x+8y=4120
Step 3: Solve for x
Solve both equations:
(4x+10y=3650)(Multiply by 4)
(5.2x+8y=4120)(Multiply by 5)
16x+40y=14600
26x+40y=20600
Subtract:
10x=6000
x=600
Final Answer: 600
15. If α and β are the roots of the equation 2x² + 5x + k = 0, and 4(α² + β² + αβ) = 23, then which of the following is true?
- k2 – 3k + 2 = 0
- k2 + 3k – 2 = 0
- k2 – 2k + 3 = 0
- k2 – 2k – 3 = 0
Given quadratic equation:
2x2 + 5x + k = 0
Roots: α and β
Step 1: Use Vieta’s Formulas
α+β = −5/2, αβ= k/2
Step 2: Given Condition
4(α2 + β2 + αβ) = 23
Using identity:
α2 + β2 = (α+β)2 − 2αβ
Substituting values:
(25/4 − 𝑘) + 𝑘/2 = 25/4 −k + k/2
Multiply by 4:
25−4k+2k=23
25−2k=23
2k=2⇒k=1
Step 3: Check the Correct Equation
Substituting k = 1 in given options,
k2 −3k+2=12 −3(1)+2=0
Thus, the correct answer is:
k2 −3k+2=0
Continue your learning journey and remain well-prepared. Best of luck!


