
TCS NQT 2025 Pattern Analysis | Big Change, All Shift Analysis, Latest Asked Questions, Cut Off
TCS NQT 2025 Pattern Analysis , In this blog we are going to discuss about TCS NQT 2025 Latest pattern and Important topics and asked questions.

TCS NQT 2025 Pattern Analysis: Exam Check-in Process
| Step | Details |
| Check-in Time | 7:30 AM (Arrived by 7:00 AM, waited 30 minutes) |
| Required Documents | Admit card |
| ID Proof Checks | Two ID checks |
| Floor Information | Floors clearly marked (e.g., 203-400 on Floor 1), assistance available |
| Validation Process | Face and thumbprint validation; provided lab and desk number |
| COVID Declaration Form | Must include a photo (can be pasted at home) |
| Login Assistance | Help available for login and password |
| Exam Start Time | 9:10 AM |
If you’re looking to streamline your preparation and avoid the hassle of juggling multiple resources, come join us for a comprehensive solution that brings everything you need together in one place!
Crack Your TCS NQT With Us!
TCS NQT 2025 Pattern Analysis: Topic wise Analysis
Section 1: Quantitative Aptitude
| Topic | Number of Questions |
| Averages | 2 |
| Ages | 2 |
| Percentages | 2 |
| Speed and Distance | 2 |
| Statistics | 2 |
| Number System | 1 |
| Simplification | 1 |
| LCM | 1 |
| Time Speed Distance | 1 |
| SI & CI | 1 |
| Mean | 1 |
| Profit & Loss | 1 |
| Time and Work | 1 |
| Weights | 1 |
| Volume | 1 |
| Ratio Partnership | 1 |
| Mensuration | 1 |
| TITA Question | 1 |
Section 2: Verbal Ability
| Topic | Number of Questions |
| Reading Comprehension (2 Passages) | 7-8 |
| Synonyms | 1 |
| Grammar-based Questions | 4-5 |
| Error Correction | 2-3 |
| Meaning Replacement | 2 |
| Sentence Arrangement | 2-3 |
**Para jumbles will be TITA based.
Section 3: Logical Reasoning
| Topic | Number of Questions |
| Syllogism | 2-6 |
| Seating Arrangement | 2-4 |
| Chinese Coding | 1-3 |
| Pair Identification (Vowel/Consonant Order) | 2 |
| Pattern Recognition (Images) | 2 |
| Coding/Decoding | 2 |
| Odd Man Out | 2 |
| Direction | 2 |
| Data Sufficiency | 2 |
| Blood Relation | 1 |
| Circular Seating Arrangement (TITA) | 1 |
Section 4: Advanced Quantitative
| Topic | Number of Questions |
| TITA Questions | 5-6 |
| Coding Decoding | 2 |
| Eligibility | 2 |
| Time Speed Distance | 1 |
| Profit & Loss | 1 |
| Data Interpretation | 1 |
| Syllogism | 1 |
| Venn Diagram | 1 |
| Quadratic Equation | 1 |
**Most of the TITA questions are asked in this section.
Section 5: Coding
| Question Number | Difficulty Level | Time Allotted |
| 1st Question | Easy | 35 minutes |
| 2nd Question | Medium | 55 minutes |
- TCS has allocated specific time limits for each coding section within the 90-minute duration this time.
- In both the questions there were 7 test cases.
TCS NQT 2025 Cut Off
Understanding the cut-off criteria is crucial to assess your readiness for the exam. The cut-off varies yearly based on factors such as the number of applicants and difficulty level. However, this is the expected cut off for TCS NQT 2024 on April 2024:
| Sections | Expected Cut Off |
| Numerical Ability | 8-10 Q |
| Logical Reasoning | 10-12 Q |
| Verbal Ability | 10-15 Q |
| Advanced Quantitative + Reasoning Ability | 6-7 Q |
| Advanced Coding | *** |
***TCS NQT 2025 Role wise Cut Off:
| Role | Cut off |
| Ninja | Only Foundation section cleared |
| Digital | Foundation + Advanced Aptitude+ 1 coding question |
| Prime | Foundation + Advanced Aptitude+ 2 coding question |
Note: These are approximate numbers. The actual cut-off may vary slightly based on the batch.
TCS NQT 2025 Expected Result:
| Exam Details | Time Taken |
| Written Exam to Interview | After the written exam TCS generally takes 20 days to 1 month to declare the result. (This may vary dependind upon wheather the hiring is On campus or Off campus) |
| Interview to Final Selection | Following the interview TCS generally takes 15-20 days to declare the final selection result. |
Q1. LCM of 18, 45, 408, 255.
LCM(18, 45, 408, 255.) = 6120
Steps:
Prime factorization of the numbers:
18 = 2 * 3 * 3
45 = 3 * 3 * 5
408 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 3 * 17
255 = 3 * 5 * 17
LCM(18, 45, 408, 255.)
=2×2×2×3×3×5× 17
= 6120
Q2. Difference between the SI and CI of 20000 with 10% rate for 3 years.
To find the difference between Simple Interest (SI) and Compound Interest (CI) for a principal amount of ₹20,000 at an interest rate of 10% for 3 years, we need to calculate both SI and CI.
(CT-SI)3= P*r2*(300+r)/1003
=2000*102*(300+10)/1003
620
The difference between the Compound Interest (CI) and the Simple Interest (SI) is approximately ₹620.
Q3. Sum of 2760 with 5% CI rate for 5 years.
A = 𝑃×(1+𝑅/100)𝑇
Where:
A = Final amount (sum)
P = Principal amount = ₹2,760
R = Rate of interest = 5%
T = Time = 5 years
Let’s calculate the final amount
𝐴=2760*(1+5/100)5
The sum after 5 years with a compound interest rate of 5% on ₹2,760 will be approximately ₹3,522.54.
Q4. A and B invested 20000 and 40000 . Total profit is 15000. A get his share plus salary 7000. What is the amount of A’s salary.
Ratio of A’s investment to B’s investment =20000:40000=1:2
Calculate A’s share in the total profit: The total profit is ₹15,000, so the total ratio is 1 + 2 = 3 parts.
A’s profit share =1/3×15000=5000
Determine A’s salary: A receives ₹7,000 in total (his profit share plus salary). Therefore, his salary is:
A’s salary=7,000−5,000=2,000
Final Answer:
A’s salary is ₹2,000.
Q5. A train travel a distance with 70kmph for 1 hour. Then travel a distance with pkm/hr for 1 and 1/2 hours. If the avg speed is 64km/hr then the value of ‘p’?
To find the value of 𝑝, we can use the formula for average speed. The average speed is defined as:
Average Speed = Total Distance/Total Time
Step 1: Calculate the distance traveled by the train at 70 km/h for 1 hour.
Distance 1 =Speed×Time=70km/h×1h=70km
Step 2: Calculate the distance traveled by the train at
Distance 2 =p km/h×1.5h=1.5p km
Step 3: Calculate the total distance and total time.
Total Distance=Distance 1 +Distance 2 =70+1.5pkm
Total Time=1h+1.5h=2.5h
Step 4: Set up the equation using the average speed.
Given that the average speed is 64 km/h, we can set up the equation as follows:
64= (70+1.5p)/ 2.5
Step 5: Solve for
P is 60 km/h.
Q6. Case 1 where mode is ‘M’. Median and mean is 12 and 7. Case 2 where mode is ‘N’ and Median and mean is 22 and 18. Then what is the mean of M, N?
| In Case 1 | In Case 2 |
| Median = 12 Mean = 7 Mode = M Mode = 3Median-2Mean M=36-14 M=22 | Median = 22 Mean = 18 Mode = N Mode = 3Median-2Mean N=66-36 N=30 |
Mean of M and N= (22+30)/2=26
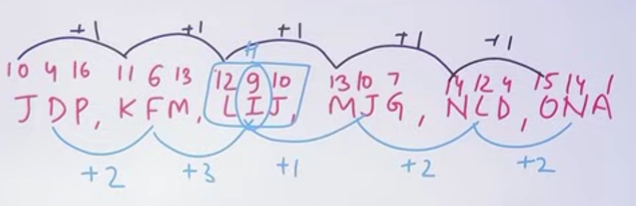
Q7. Find the odd one
JDP, KFM, LIJ, MJG, NLD, ONA.
Q8. NPRT : GHIJ :: LXTP: ?
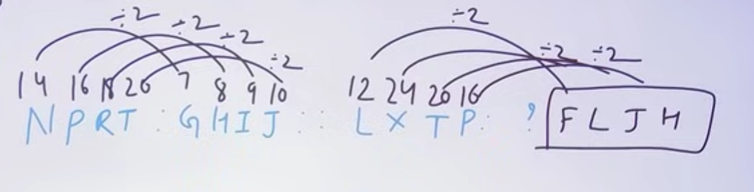
For Video solution: Click Here!
TCS NQT 3rd October 2024 CODING QUESTIONS
Q1. Find the Total minutes of exercise done and it’s average for a week.
Input:
Day 1 exercise duration: 25
Day 2 exercise duration: 26
Day 3 exercise duration: 23
Day 4 exercise duration: 15
Day 5 exercise duration: 14
Day 6 exercise duration: 38
Day 7 exercise duration: 44
Result: 185 26.4
Solution –
C++ code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
Using namespace std;
Int main() {
Int duration, sum = 0;
For(int I = 0; I < 7; i++) { Cout << “Day “ << i+1 << “ exercise duration: “; Cin >> duration;
Sum += duration;
}
Double avg = static_cast(sum) / 7;
Cout << “\nTotal minutes: “ << sum;
Cout << “\nAverage minutes per day: “ << avg;
Return 0;
}
Java Code
import java.util.Scanner;
Public class Main {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Int sum = 0, duration;
For (int I = 0; I < 7; i++) {
System.out.print(“Day “ + (I + 1) + “ exercise duration: “);
Duration = scanner.nextInt();
Sum += duration;
}
Double avg = (double) sum / 7;
System.out.println(“\nTotal minutes: “ + sum);
System.out.println(“Average minutes per day: “ + avg);
Scanner.close();
}
}
If the loop runs for n days instead of a fixed 7 days:
The time complexity is O(n) due to the loop running n times, while the space complexity is O(1) as only constant memory is used.
For Week : TC is O(1)
SC is O(1)
Q2. (print the total number of palindrome between the given range m and n,0<=m,n<=1000)
For example input1 (lowest range =0 and Highest range =20)
Input: 0 20
Output: 11
Reason: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11
These numbers are palindrome
Solution –
C++ Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
Using namespace std;
Bool is_palindrome(int n) {
Int original = n, reversed = 0;
While (n > 0) {
Reversed = reversed * 10 + (n % 10);
N /= 10;
}
Return original == reversed;
}
Int main() {
Int m, n, count = 0;
Cout << “Enter the range of m and n: “; Cin >> m >> n;
For (int I = m; I <= n; i++) {
If (is_palindrome(i)) count++;
}
Cout << “Number of palindromes: “ << count;
Return 0;
}
Java Code
import java.util.Scanner;
Public class Main {
Public static boolean isPalindrome(int n) {
Int original = n, reversed = 0;
While (n > 0) {
Reversed = reversed * 10 + (n % 10);
N /= 10;
}
Return original == reversed;
}
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter the range of m and n: “);
Int m = scanner.nextInt();
Int n = scanner.nextInt();
Int count = 0;
For (int I = m; I <= n; i++) {
If (isPalindrome(i)) {
Count++;
}
}
System.out.println(“Number of palindromes: “ + count);
Scanner.close();
}
}
The time complexity is O(k * log n), where k is the range size and log n is the number of digits in the largest number, while the space complexity is O(1) since no additional data structures are used.


